pleural effusion cat lymphoma
Ing 65 feline pleural effusions where diagnosis was. Viral infection of the lungs.

Read About Oncology In This Article By Leanne N Twomey And Rick A Alleman
Twisting of the lung.

. Pleural Effusion and Hemothorax The pleural cavity is composed of two potential spaces separated by a fenestrated mediastinum. The pleural cavity in the dog usually contains less than 5 cc of fluid and a similar amount in the healthy cat is assumed. Found with right congestive heart failure obstruction to lymphatic drainage by tissue adhesions in pleural space lung lobe torsion neoplasms and abdominal contents herniating.
It helps the lungs move in your chest as you breathe. World Small Animal Veterinary Association World Congress Proceedings 2004. College of Veterinary Medicine Colorado State University.
Only after the cat has stabilized will an exclusionary diagnosis - utilizing X-rays blood tests and a fecal examination - be undertaken to definitively identify the source of the respiratory distress following which an appropriate treatment plan will be established. Form of feline lymphoma arises from diffuse mucosal associated lymphoid tissue MALT of the small. EATCL type II is associated with indolent clinical behavior and prolonged survival time and.
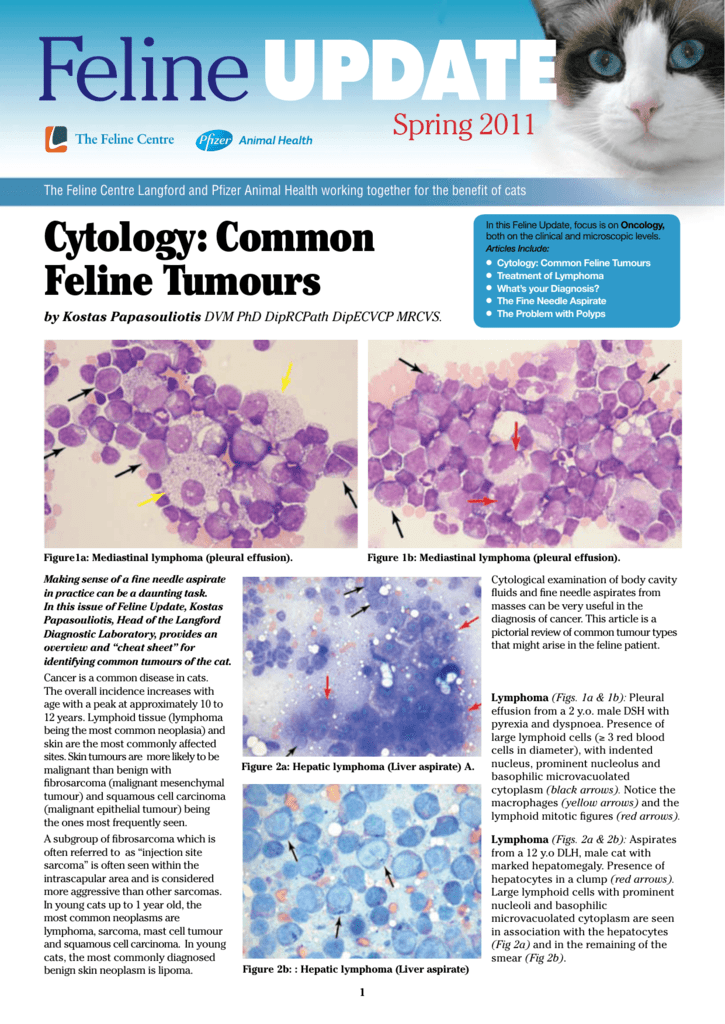
You have pleura surrounding your lungs and lining the inside of your chest. Pleural effusion due to lymphomas either primary or otherwise is considered as one of the factors adversely influencing overall survival. Pertinent findings included a high occurrence of pleural effusion with mediastinal lymphoma and other types of.
A small amount of fluid in this area is normal. Or if pleural effusion is suspected fluid will be drained from its chest. Pleural involvement with lymphoma can occur in two situations.
Trauma is an uncommonly recognized cause of chylothorax in dogs and cats because the thoracic duct heals rapidly after injury and the effusion resolves within 1 to 2 weeks without treatment. Bacterial infection of the lungs. Feline mediastinal lymphoma commonly occurs in young cats with a median age at diagnosis of three years and has commonly been associated with a positive FeLV status.
However transudative effusion can occur from heart failure or venous compression. Certain conditions can cause pleural effusion in cats. Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity.
Tumors in the lungs or chest wall can lead to pleural effusion. Lymphomatous pleural effusions are usually exudative. This syndrome is caused by infection with a mutated form of a feline coronavirus.
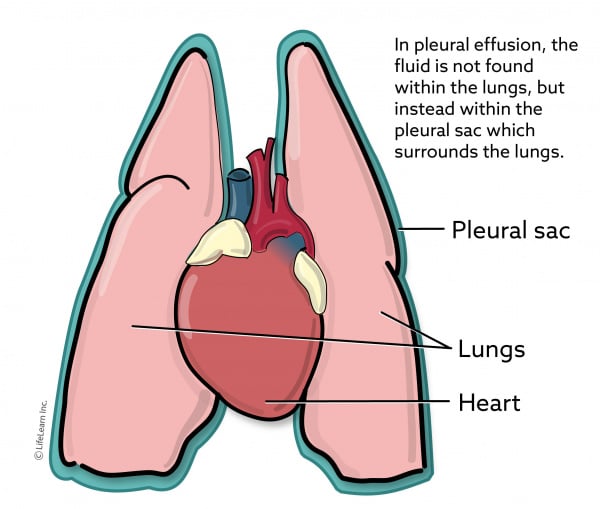
1 However solid pleural involvement is less common and is usually a secondary event. When FIP affects the chest cavity pleural effusion results. A build-up of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall is called a pleural effusion This area of the body is called the pleural spacePleura is another word for membrane.
Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at presentation. The most common causes for pleural effusion in all 380 cats were found to be CHF n155 408 and neoplasia n98 258. Below are some of the most common causes of fluid build-up in cats lungs.
In pleural effusion the lungs are floating in a chest that is full of fluid. Low levels of protein in the blood. Eighty-two cases of feline pleural effusion were identified and reviewed to assess the type of fluid underlying disease process predisposing conditions historical and physical examination findings laboratory and cytology data response to treatment and outcome.
Excess fluid accumulation may be the result of increased. The pleural effusion consisted of 88 lymphocytes with a mixture of small and intermediate forms Question 1 with fewer non-degenerate neutrophils and rare macrophages Figure 4. In pleural effusion the fluid is not found within the lungs but instead within the pleural sac.
Other causes included pyothorax idiopathic chylothorax trauma FIP nontraumatic diaphragmatic hernia vasculopathy uremic pleuritis hypoproteinemia and vitamin K antagonist toxicity. Consists of small to intermediate-sized lymphoma cells which is consistent with current terminology that. Either way the prognosis is not good.
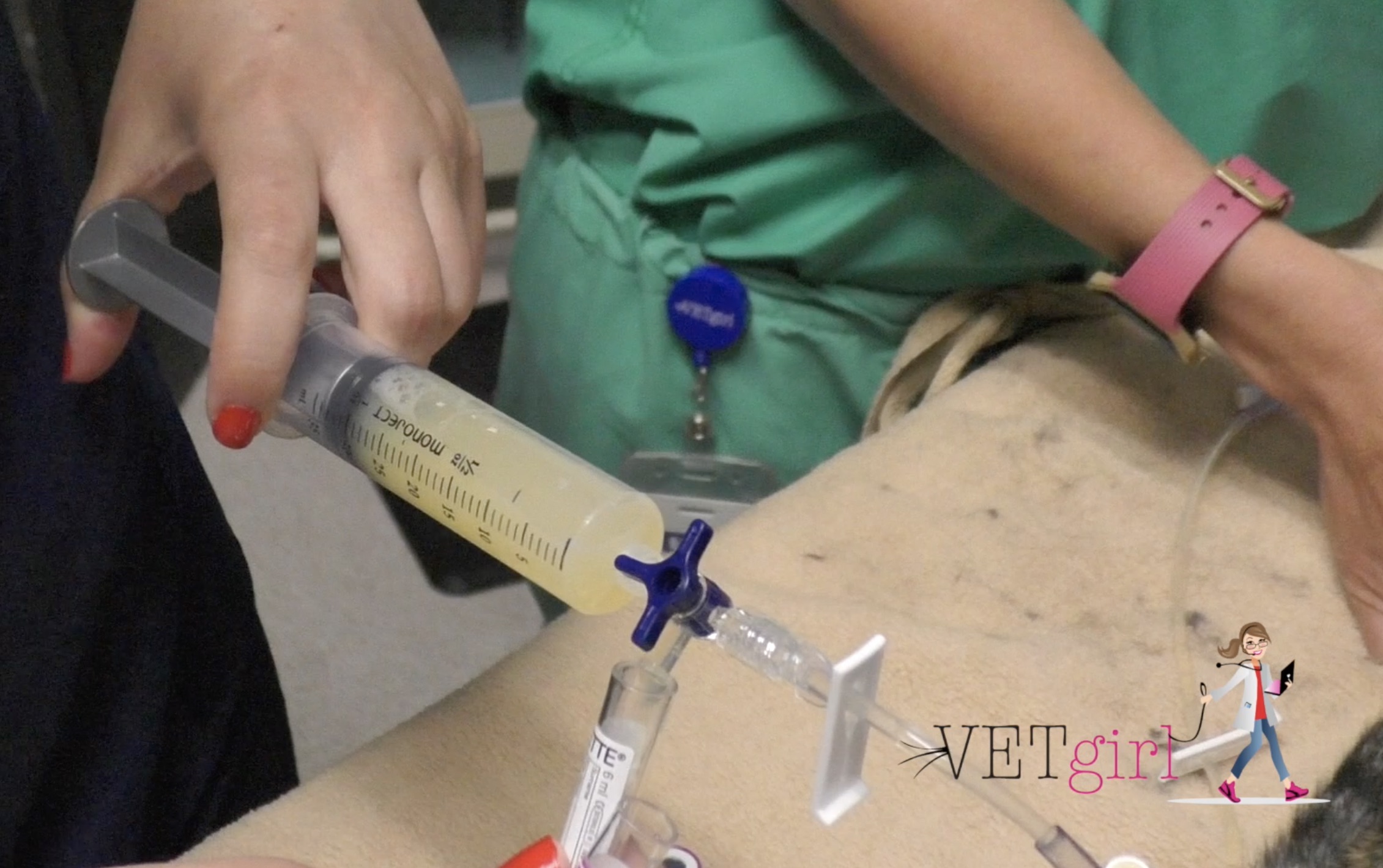
This fluid occupies space within the chest keeping the lungs from expanding as fully as they should. Careful handling and prompt and adequate stabilisation incorporating supplemental oxygen and therapeutic thoracocentesis is essential to avoid respiratory failure. Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood.
Some of the symptoms of pleural effusion include the following. Secondary involvement of the pleura with lymphoma. Rapid breathing Breathing with an open mouth Lethargy Lack of appetite Weight loss Chest pains Fever Coughing Unusual positions while sitting or lying down Blue tongue or gums.
Eric Monnet DVM PhD FAHA DACVS ECVS. Primary pleural lymphomas are extremely rare and in a series reported by Burgener and Hamlin pleural plaques were seen in less then 4 of cases. Abnormal functioning of the lymphatic system.
Pleural effusion is a common finding in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma with a reported incidence of 16 to 20. The thoracic cavity is lined entirely by a serous membrane known as pleura. Up to 20 cash back With pleural effusion youre usually dealing with one of two things- Lymphoma cancer or CHF congestive heart failure.
Chylous effusion Pericardial fluid. Fort Collins CO USA. The presence of pleural effusion at the time of presentation is not only associated with extremely poor outcome of lymphomas it is also a predictor of disease relapse after chemotherapy and decreased survival.
Alterations in the cats blood pressure and protein. Pleural disease in non-Hodgkins lymphoma is well documented and commonly presents with pleural effusions in 20 of patients. Among them 60 account for DLBC lymphoma.
Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity which is lined by a membrane -- the pleural lining. Cats of the Siamese breed are overrepresented for both mediastinal lymphoma young cats and chylothorax. We try to get these cats to survive 9-12 months.
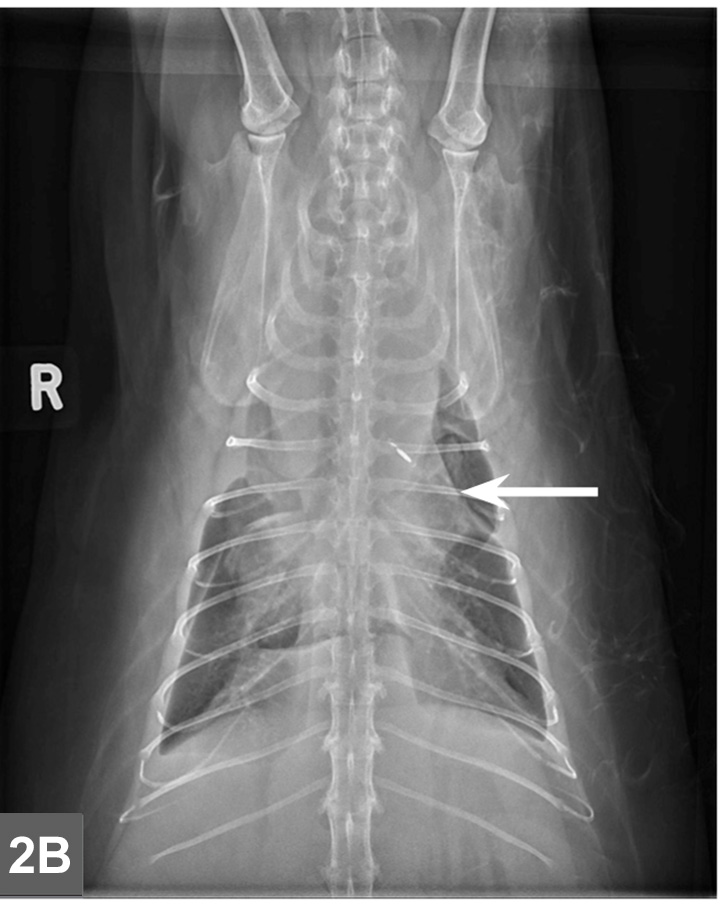
The pleura is divided into visceral pleura which. The most common presenting clinical signs include dyspnoea tachypnoea inappetence and cough with half of the cats presenting with pleural effusion at diagnosis. Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
This occurs in cats either because too little fluid is being absorbed in the pleural cavity or because too much fluid is being produced in the pleural cavity. In some cats infection with mutated coronavirus can lead to blood vessel damage which results in fluid leakage. Chylothorax has been reported in a cat after ligation of the left brachycephalic vein.
Feline infectious peritonitis.
Pleural Effusion In Cats Vca Animal Hospitals
Cytology Common Feline Tumours
Pleural Effusion In The Cat Hellenic Journal Of Companion Animal Medicine

Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief

Effusion Cytology Clinician S Brief
Small Intestine Neoplasia In Cats Vetlexicon Felis From Vetstream Definitive Veterinary Intelligence

Figure 3 From Pericardial Lymphoma In Seven Cats Semantic Scholar
Causes Of Pleural Effusion In Cats Vetgirl Veterinary Continuing Education Blog
Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief
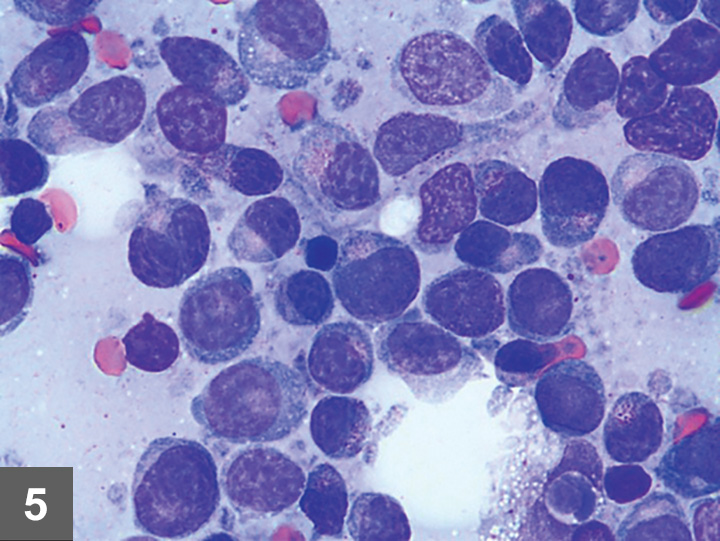
Feline Lymphoma Clinician S Brief

Pleural Effusion Fine Needle Aspirate Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma Download Scientific Diagram

Chylous Effusion In A Cat Clinician S Brief

Read About Oncology In This Article By Leanne N Twomey And Rick A Alleman
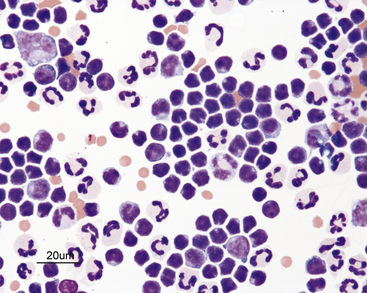
Effusions Abdominal Thoracic And Pericardial Veterian Key

Effusion Cytology Clinician S Brief

Lymphorrhagic Effusion Collected From The Pleural Space Nu Merous Download Scientific Diagram
Pleural Effusion In The Cat Hellenic Journal Of Companion Animal Medicine
